CesiumJS is a powerful open-source JavaScript library for 3D geospatial visualization on the web. It allows developers to build interactive globes and maps that handle massive datasets, visualize terrain, and display real-time simulations. From aerospace and defense to urban planning and GIS applications, CesiumJS is widely used to bring geospatial data to life in the browser.
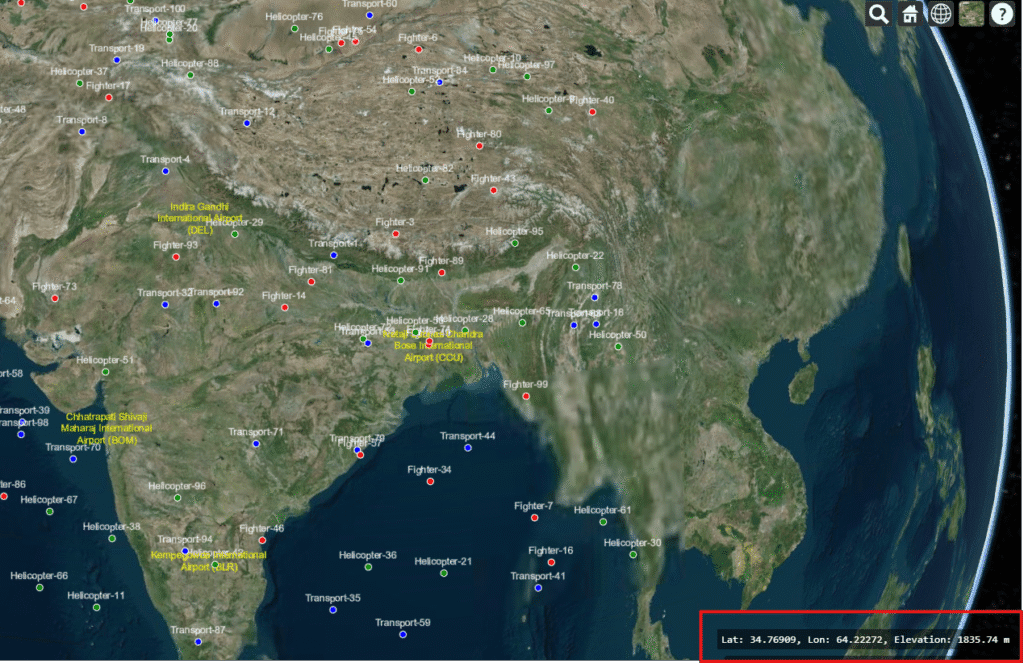
One common requirement when working with maps or 3D globes is to display the current mouse coordinates — latitude, longitude, and elevation. This helps users track precise geographic positions directly on the map. In this post, we’ll build a simple example that shows these values in real time as you move your mouse across the globe.
Step 1: Webpage Code
Here’s a complete webpage you can save as index.html and run in your browser (after placing the Cesium/ library folder in your project):
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>CesiumJS Mouse Coordinates Example | Manya Technologies</title>
<meta name="description" content="Learn how to display real-time latitude, longitude, and elevation of the mouse position in CesiumJS." />
<!-- CesiumJS Library -->
<script src="./Cesium/Cesium.js" defer></script>
<link href="./Cesium/Widgets/widgets.css" rel="stylesheet">
<style>
body, html {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
overflow: hidden;
}
#cesiumContainer {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
display: block;
}
#mouseLocation {
position: absolute;
bottom: 10px;
left: 10px;
padding: 6px 10px;
background: rgba(0,0,0,0.6);
color: #fff;
font-family: monospace;
border-radius: 4px;
font-size: 14px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="cesiumContainer"></div>
<div id="mouseLocation">Lat: -, Lon: -, Elevation: -</div>
<script>
function initCesium() {
// Initialize Cesium Viewer
const viewer = new Cesium.Viewer("cesiumContainer", {
terrainProvider: Cesium.createWorldTerrain()
});
// Event handler for mouse movement
const handler = new Cesium.ScreenSpaceEventHandler(viewer.scene.canvas);
const mouseLocation = document.getElementById("mouseLocation");
handler.setInputAction((movement) => {
const cartesian = viewer.scene.pickPosition(movement.endPosition);
if (Cesium.defined(cartesian)) {
const cartographic = Cesium.Cartographic.fromCartesian(cartesian);
const lat = Cesium.Math.toDegrees(cartographic.latitude).toFixed(5);
const lon = Cesium.Math.toDegrees(cartographic.longitude).toFixed(5);
const height = cartographic.height.toFixed(2);
mouseLocation.innerText = `Lat: ${lat}, Lon: ${lon}, Elevation: ${height} m`;
} else {
mouseLocation.innerText = `Lat: -, Lon: -, Elevation: -`;
}
}, Cesium.ScreenSpaceEventType.MOUSE_MOVE);
}
window.onload = initCesium;
</script>
</body>
</html>
Step 2: Run the Example
- Save the file as
index.html. - Place it in the same folder as your CesiumJS build (
Cesium/). - Open it in a browser.
As you move your mouse across the globe, you’ll see the latitude, longitude, and elevation update instantly.
Conclusion
By adding just a few lines of code, you can enrich your CesiumJS applications with real-time geographic feedback. This is especially valuable for GIS platforms, defense simulations, aviation trackers, and geospatial analysis tools. Check out live demo at https://cesiumjs.manyatechnologies.com/
At Manya Technologies, we specialize in building custom geospatial applications, real-time simulations, and advanced visualization tools using technologies like CesiumJS, Qt, QGIS, and PostGIS. If you’d like to implement solutions like this in your project, feel free to contact us — we’d be happy to help.